7 Yu JS, Ashman CJ, Jones G. The POLPSA lesion: MR imaging findings with arthroscopic correlation in patients with posterior instability. To provide the highest quality clinical and technology services to customers and patients, in the spirit of continuous improvement and innovation. Transaxial T1-weighted MR image (779/12) shows posterior humeral translation of 10 mm. 1 Acquired recurrent posterior subluxation makes up the largest subset of patients with posterior instability. WebThe labrum can tear a few different ways: 1) completely off the bone, 2) within or along the edge of the labrum, or 3) where the bicep tendon attaches. View Magdalena Chmiel-Nowak's current disclosures, see full revision history and disclosures, doi:10.1148/radiographics.20.suppl_1.g00oc03s67, pain or discomfort (usually a precise point of pain cannot be located). (4a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a severely retroverted glenoid (arrowheads) and posterior glenoid hypoplasia with a hypertrophied posterior labrum (arrow).  However, for successful treatment there must be a clear understanding of underlying soft tissue abnormalities. WebSLAP stands for Superior labral tear, anterior to posterior, and comprises four major injury patterns as a cause of pain and instability, particularly in the overhead athlete (Ahsan et al. A number of biomechanical studies have demonstrated the importance of both posterior and anterior capsuloligamentous structures in maintaining static posterior stability. In general, throwing athletes can return to early interval throwing 3 to 4 months after surgery. How long you require a sling depends upon the severity of your injury. True dysplasia should be visible on at least two axials slices cephalad to the most inferior slice of the glenoid (Fig. 2011 Sep;27(9):1304-7.
However, for successful treatment there must be a clear understanding of underlying soft tissue abnormalities. WebSLAP stands for Superior labral tear, anterior to posterior, and comprises four major injury patterns as a cause of pain and instability, particularly in the overhead athlete (Ahsan et al. A number of biomechanical studies have demonstrated the importance of both posterior and anterior capsuloligamentous structures in maintaining static posterior stability. In general, throwing athletes can return to early interval throwing 3 to 4 months after surgery. How long you require a sling depends upon the severity of your injury. True dysplasia should be visible on at least two axials slices cephalad to the most inferior slice of the glenoid (Fig. 2011 Sep;27(9):1304-7.  A fat suppressed proton density-weighted axial image (1a) is provided. On CT it is easy to appreciate the osseus fragment of the anterior glenoid (arrow). This is especially the case in older adults, because our cartilage becomes more brittle with age. Diagnosis can be made clinically with positive posterior labral provocative tests and confirmed with MRI studies of the shoulder. 5). Mr Watson will decide the best repair option based upon the type of tear you have, as well as your age, activity level, and the presence of any other injuries seen during the surgery.
A fat suppressed proton density-weighted axial image (1a) is provided. On CT it is easy to appreciate the osseus fragment of the anterior glenoid (arrow). This is especially the case in older adults, because our cartilage becomes more brittle with age. Diagnosis can be made clinically with positive posterior labral provocative tests and confirmed with MRI studies of the shoulder. 5). Mr Watson will decide the best repair option based upon the type of tear you have, as well as your age, activity level, and the presence of any other injuries seen during the surgery.  WebThe labrum of the shoulder is made of soft tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray. no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Those undergoing open surgery should expect more pain, longer recovery, and in some cases incomplete shoulder rotation. Musculoskeletal Imaging,The Requisites (Expert Consult- Online and Print),4. MR interpreters should be aware that at The images show a subtle Bankart fracture (arrows). Musculoskeletal MRI. In the ABER position however there is tension on the antero-inferior labrum by the stretched anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament and you have more chance to detect the tear. Posterior dislocations account for 2-4% of all shoulder dislocations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (Left)An MRI image of a healthy shoulder.(Right)This MRI image shows a tear in the labrum. Some SLAP injuries require cutting the biceps tendon attachment. <>>>
Case 7: type II with greater tuberosity fracture, Cas 10: type IV - double "Oreo cookie" sign, View Frank Gaillard's current disclosures, View Doaa Faris Jabaz's current disclosures, see full revision history and disclosures, in younger patients (<40 years of age) these are associated with, in older patients (>40 years of age) they are associated with, type I tears are usually asymptomatic and do not require treatment, type II tears require surgical reattachment, type III tears usually require resection of the bucket handle tear, high T2 signal or contrast curves laterally, high signal or contrast extends posteriorly to the biceps anchor, 1. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle Normal shoulder MRI. 3 0 obj
174 no. Due to these recurrent dislocations significant bone loss and erosion of the anterior glenoid rim may occur, which maintains the unstable situation. The arrow points to the cartilage defect. Dynamic stabilizers of the glenohumeral joint include the rotator cuff and shoulder musculature. Hottya GA, Tirman PF, Bost FW, Montgomery WH, Wolf EM, Genant HK. Locked posterior subluxation of the shoulder: diagnosis and treatment. Philip Robinson. A mid-substance tear of the posterior capsule is present with the medial component appearing lax and retracted (arrow). The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal 14:5-14,2001. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 74A:53-66, 1992. 6. Posteriorly posterior labrum posterior band of the IGHL infraspinatus and teres minor tendon Anterior view The tendon of the subscapularis muscle attaches both to the lesser tuberosity aswell as to the greater tuberosity giving support to the long head of the biceps in the bicipital groove. endobj
When the ball slips toward the back of the body, it leads to "posterior instability.". It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. 4. Although athletes are most prone to labral tears, people who experience a traumatic event such as falling down a flight of stairs are also at risk. Notice the detatched labrum at the 6-9 o'clock position on the sagittal MR-arthrogram. In a SLAP injury, the top (superior) part of the labrum is injured. . Fig. A posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) is also present (arrowhead), and a bone bruise is seen within the anterior humeral head (asterisk). Wearing a sling will protect your shoulder after surgery. Sectioning of the rotator interval capsule has been shown to increase posterior and inferior translation of the humeral head.3. Specific exercises will restore movement and strengthen your shoulder. There is also a Hill-Sachs defect (red arrow). Drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen reduce pain and swelling. Continue with the images in ABER-position. MRA( ) . Patients with periosteal sleeve avulsions, such as the POLPSA, are more likely to be symptomatic.9. These tears include numerous variations designated by acronyms similar to those used for the more commonly seen anterior labral tears. These labral tears make the shoulder unstable and susceptible to repeated dislocations. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. Tear of the posterior shoulder stabilizers after posterior dislocation: MR imaging and MR arthrographic findings with arthroscopic correlation. Finally there is a medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the 3-6 o 'clock position, i.e. 6 Fery A: Results of treatment of anterior serratus paralysis. AJR June 2000 vol. MR interpreters should be aware that at 8. The labrum acts both as a bumper and as an attachment point for the ligaments of the shoulder. Sports Health 2011 May, 3(3):253-263, Cooper A. Sagittal MR-arthrogram demonstrates the superior extension of the Bankart tear. Glenoid hypoplasia is associated with an increased incidence of posterior labral tears and has been identified as a potential cause of posterior instability and accelerated degenerative joint disease.4 Glenoid retroversion describes an excessively posteriorly directed glenoid articular surface, which can contribute to posterior instability (Figure 4a). 2. endobj
Check for errors and try again. Below: an MRI arthrogram showing injection of contrast into the shoulder joint. AJR 1998; 171:763-768. MR interpreters should be aware that at times capsular tears are quite subtle. Patients most at risk for posterior instability include athletes such as weight lifters, throwers, tennis players, and swimmers. WebType 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. Bankart-lesions and variants like Perthes and ALPSA are injuries to the anteroinferior labrum. This resulted in both a Hill-Sachs impression fracture on the posterior aspect of the humeral head (blue arrow) and an impression fracture on the anterior aspect as a result of posterior dislocation (red arrow). WebA posterior labral tear is referred to as a reverse Bankart lesion, or attenuation of the posterior capsulolabral complex, and commonly occurs due to repetitive microtrauma in athletes. This exercise program can be continued anywhere from 3 to 6 months, and usually involves working with a qualified physical therapist. Images of another patient with an ALPSA-lesion. If the injury is a minor Bankart tear with a dislocation, the physician (or even a team coach or patient themselves) can usually pop the shoulder back into place a process called reduction and then follow up with physical therapy to strengthen the muscles. The humeral head is almost always displaced anteriorly and medially below the coracoid process. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an Bankart lesions are labral tears without an osseus fragment. At the time the article was created Magdalena Chmiel-Nowak had no recorded disclosures. AJR Am J Roentgenol. Recurrent posterior subluxation is the most common form of posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency. Complications. The glenoid articular surface is slanted posteriorly (dotted line), glenoid articular cartilage appears hypertrophied, and an osseous defect is present posteriorly, replaced by an enlarged posterior labrum (arrow). In: Post M, Morrey BF, Hawkins RJ, editors. In patients with glenoid deficiency or large impaction defects, osteotomies and osseous augmentation procedures may be required. Constant balancing of static and dynamic stabilizers is required to maintain glenohumeral stability. Skeletal Radiol 2000; 29:204-210. An acute SLAP injury may result from: People who participate in repetitive overhead sports, such as throwing athletes or weightlifters, can experience labrum tears as a result of repeated shoulder motion. xZ[oF~GxiWEi$zI)3PD97e./o]7,?8bqi&VP>}e Rotator cuff tears in the context of posterior shoulder instability or dislocation were once thought to be rare. MR interpreters should be aware that at Your doctor may recommend surgery if your pain does not improve with nonsurgical methods. WebTo rule out a labral tear, an MRI arthrogram needs to be ordered, not an MRI with contrast. The retracted end of the subscapularis (asterisk) is also visible compatible with a full thickness tear. Notice how this high signal continues posteriorly, which means that it is a SLAP-lesion. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
WebThe labrum of the shoulder is made of soft tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray. no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Those undergoing open surgery should expect more pain, longer recovery, and in some cases incomplete shoulder rotation. Musculoskeletal Imaging,The Requisites (Expert Consult- Online and Print),4. MR interpreters should be aware that at The images show a subtle Bankart fracture (arrows). Musculoskeletal MRI. In the ABER position however there is tension on the antero-inferior labrum by the stretched anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament and you have more chance to detect the tear. Posterior dislocations account for 2-4% of all shoulder dislocations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (Left)An MRI image of a healthy shoulder.(Right)This MRI image shows a tear in the labrum. Some SLAP injuries require cutting the biceps tendon attachment. <>>>
Case 7: type II with greater tuberosity fracture, Cas 10: type IV - double "Oreo cookie" sign, View Frank Gaillard's current disclosures, View Doaa Faris Jabaz's current disclosures, see full revision history and disclosures, in younger patients (<40 years of age) these are associated with, in older patients (>40 years of age) they are associated with, type I tears are usually asymptomatic and do not require treatment, type II tears require surgical reattachment, type III tears usually require resection of the bucket handle tear, high T2 signal or contrast curves laterally, high signal or contrast extends posteriorly to the biceps anchor, 1. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle Normal shoulder MRI. 3 0 obj
174 no. Due to these recurrent dislocations significant bone loss and erosion of the anterior glenoid rim may occur, which maintains the unstable situation. The arrow points to the cartilage defect. Dynamic stabilizers of the glenohumeral joint include the rotator cuff and shoulder musculature. Hottya GA, Tirman PF, Bost FW, Montgomery WH, Wolf EM, Genant HK. Locked posterior subluxation of the shoulder: diagnosis and treatment. Philip Robinson. A mid-substance tear of the posterior capsule is present with the medial component appearing lax and retracted (arrow). The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal 14:5-14,2001. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 74A:53-66, 1992. 6. Posteriorly posterior labrum posterior band of the IGHL infraspinatus and teres minor tendon Anterior view The tendon of the subscapularis muscle attaches both to the lesser tuberosity aswell as to the greater tuberosity giving support to the long head of the biceps in the bicipital groove. endobj
When the ball slips toward the back of the body, it leads to "posterior instability.". It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. 4. Although athletes are most prone to labral tears, people who experience a traumatic event such as falling down a flight of stairs are also at risk. Notice the detatched labrum at the 6-9 o'clock position on the sagittal MR-arthrogram. In a SLAP injury, the top (superior) part of the labrum is injured. . Fig. A posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) is also present (arrowhead), and a bone bruise is seen within the anterior humeral head (asterisk). Wearing a sling will protect your shoulder after surgery. Sectioning of the rotator interval capsule has been shown to increase posterior and inferior translation of the humeral head.3. Specific exercises will restore movement and strengthen your shoulder. There is also a Hill-Sachs defect (red arrow). Drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen reduce pain and swelling. Continue with the images in ABER-position. MRA( ) . Patients with periosteal sleeve avulsions, such as the POLPSA, are more likely to be symptomatic.9. These tears include numerous variations designated by acronyms similar to those used for the more commonly seen anterior labral tears. These labral tears make the shoulder unstable and susceptible to repeated dislocations. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. Tear of the posterior shoulder stabilizers after posterior dislocation: MR imaging and MR arthrographic findings with arthroscopic correlation. Finally there is a medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the 3-6 o 'clock position, i.e. 6 Fery A: Results of treatment of anterior serratus paralysis. AJR June 2000 vol. MR interpreters should be aware that at 8. The labrum acts both as a bumper and as an attachment point for the ligaments of the shoulder. Sports Health 2011 May, 3(3):253-263, Cooper A. Sagittal MR-arthrogram demonstrates the superior extension of the Bankart tear. Glenoid hypoplasia is associated with an increased incidence of posterior labral tears and has been identified as a potential cause of posterior instability and accelerated degenerative joint disease.4 Glenoid retroversion describes an excessively posteriorly directed glenoid articular surface, which can contribute to posterior instability (Figure 4a). 2. endobj
Check for errors and try again. Below: an MRI arthrogram showing injection of contrast into the shoulder joint. AJR 1998; 171:763-768. MR interpreters should be aware that at times capsular tears are quite subtle. Patients most at risk for posterior instability include athletes such as weight lifters, throwers, tennis players, and swimmers. WebType 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. Bankart-lesions and variants like Perthes and ALPSA are injuries to the anteroinferior labrum. This resulted in both a Hill-Sachs impression fracture on the posterior aspect of the humeral head (blue arrow) and an impression fracture on the anterior aspect as a result of posterior dislocation (red arrow). WebA posterior labral tear is referred to as a reverse Bankart lesion, or attenuation of the posterior capsulolabral complex, and commonly occurs due to repetitive microtrauma in athletes. This exercise program can be continued anywhere from 3 to 6 months, and usually involves working with a qualified physical therapist. Images of another patient with an ALPSA-lesion. If the injury is a minor Bankart tear with a dislocation, the physician (or even a team coach or patient themselves) can usually pop the shoulder back into place a process called reduction and then follow up with physical therapy to strengthen the muscles. The humeral head is almost always displaced anteriorly and medially below the coracoid process. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an Bankart lesions are labral tears without an osseus fragment. At the time the article was created Magdalena Chmiel-Nowak had no recorded disclosures. AJR Am J Roentgenol. Recurrent posterior subluxation is the most common form of posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency. Complications. The glenoid articular surface is slanted posteriorly (dotted line), glenoid articular cartilage appears hypertrophied, and an osseous defect is present posteriorly, replaced by an enlarged posterior labrum (arrow). In: Post M, Morrey BF, Hawkins RJ, editors. In patients with glenoid deficiency or large impaction defects, osteotomies and osseous augmentation procedures may be required. Constant balancing of static and dynamic stabilizers is required to maintain glenohumeral stability. Skeletal Radiol 2000; 29:204-210. An acute SLAP injury may result from: People who participate in repetitive overhead sports, such as throwing athletes or weightlifters, can experience labrum tears as a result of repeated shoulder motion. xZ[oF~GxiWEi$zI)3PD97e./o]7,?8bqi&VP>}e Rotator cuff tears in the context of posterior shoulder instability or dislocation were once thought to be rare. MR interpreters should be aware that at Your doctor may recommend surgery if your pain does not improve with nonsurgical methods. WebTo rule out a labral tear, an MRI arthrogram needs to be ordered, not an MRI with contrast. The retracted end of the subscapularis (asterisk) is also visible compatible with a full thickness tear. Notice how this high signal continues posteriorly, which means that it is a SLAP-lesion. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.  Unable to process the form. The labrum of the shoulder is made of soft tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray.
Unable to process the form. The labrum of the shoulder is made of soft tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray. 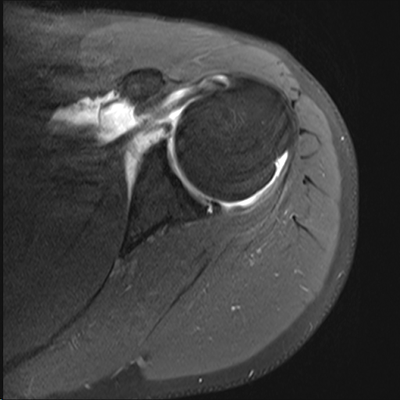 (5a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image in a patient after posterior glenohumeral dislocation demonstrates a posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) (arrow) and bone bruise (arrowheads) at the site of a reverse Hill-Sachs fracture (short arrow). Persistent pain is not typical and may point to additional pathology of the rotator cuff or biceps tendon6. WebPosterior instability of the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation. Careful physical examination is critical in diagnosing and characterizing the patients shoulder instability pattern. 2004;12(1):97-109, vi-vii. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. B. J. Manaster, David A. Both types of tears are usually accompanied by aching pain and difficulty performing normal shoulder movements. However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. The negative impact that posterior labral injuries have on a combine participants early NFL performance is important to consider especially because of how often these injuries occur among elite football players. dekalb county circuit clerk forms; zander capital management fargo, nd; patricia mcpherson interview Acute traumatic posterior shoulder dislocation: MR findings. Snyder et al. 14). In cases of severe dysplasia, advanced rounding and posterior sloping of the posterior glenoid is seen, and pronounced thickening of the labrum and other adjacent posterior soft tissues is apparent. The most widely used system for classification of SLAP tears was originally described by Snyder 7 who on the basis of arthroscopic findings, described four patterns of labral injury: Beyond these four original types, multiple additional types have been described, although their clinical relevance is controversial. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 07 Apr 2023) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-2127. (10b) A corresponding T2-weighted sagittal view in the same patient confirms the large ossification along the posteroinferior glenoid rim (arrows), compatible with a Bennett lesion. 11 ). A displaced tear of the posterior labrum (arrow) is present. J Am Med Assoc 117: 510-514, 1941. In some cases the posterior labral tear can form a flap valve and a cyst will develop. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive shoulder motion. The shoulder joint is composed of the glenoid (the shallow shoulder "socket") and the head of the upper arm bone known as the humerus (the "ball"). Bankart tears may extend to superior, but this is uncommon. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. Lee SB, Kim KJ, ODriscoll SW, Morrey BF, An KN Dynamic glenohumeral stability provided by the rotator cuff muscles in the mid-range and end-range of motion. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. Webshoulder. Direct trauma to the anterior shoulder, a posteriorly directed force on an adducted arm (fall on outstretched hand), and indirect muscle forces (seizure and electrical shock) are typical etiologies. The two most common types of labral injuries are the SLAP teartearand Bankart tear. CT arthrography has been reported to have 97.3% accuracy for detecting Bankart lesions and 86.3% for SLAP lesions 4, which makes it comparable with MR arthrography and gives the possibility to examine the patients with contraindications to an MR examination. Figure 2. On coronal images you want to make sure whether this is a variant like a labral recess or labral foramen or whether this is a SLAP. Radiology 2008; 248:185193. Snyder et al. Arthroscopy. Fluid undermines a tear of the posterior glenoid labrum (arrow) in a 42 year-old male with persistent posterior shoulder pain. 2015;6(9):660-71. At the time the article was last revised Doaa Faris Jabaz had The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. (2a) The fat-suppressed proton density-weighted axial image reveals alignment of the humeral head posteriorly relative to the glenoid, with an impaction fracture of the humeral head articular surface (red arrow). It is not clear whether the labrum is normal. 3. On the AP-view the head looks strange due to the internal rotation. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. Hip Replacement for Residual Hip Dysplasia, Long Head of Biceps Pathology (at shoulder), Shoulder Arthritis and Total Shoulder Replacement, Chronic Compartment Syndrome Fasciotomy Rehab Protocol, Rotator Cuff Repair, including Subscapularis, Rehab, Shoulder Instability Bankart Repair Rehab, Forceful pulling on the arm, such as when trying to catch a heavy object, Rapid or forceful movement of the arm when it is above the level of the shoulder, A sensation of locking, popping, catching, or grinding, Pain with movement of the shoulder or with holding the shoulder in specific positions, Pain with lifting objects, especially overhead, A feeling that the shoulder is going to pop out of joint, Pitchers may notice a decrease in their throw velocity, or the feeling of having a dead arm after pitching. The bumper helps prevent the shoulder from dislocating. There is discontinuity of the IGHL attachment on the humerus with leakage of contrast. The labrum helps to deepen the socket and stabilize the shoulder joint. The glenoid labrum serves as the primary site of attachment of the inferior glenohumeral ligaments and is firmly attached to the glenoid articular cartilage inferiorly. The head of your upper arm bone fits into a rounded socket in your shoulder blade. 2009;192: 730-735. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993 : 85-96. MRA( ) . Posterior dislocations account for 2-4% of all shoulder dislocations. 11 ). Patients who undergo arthroscopic repair can expect shorter recovery times and less pain. Images of a patient with an ALPSA-lesion. 1994 May; 3(3):173-90. endobj
Mr Watson will discuss with you when it is safe to return to sports activity. However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. 15,16). Posterior labrum periosteal sleeve avulsion (POLPSA) lesion with associated posterior glenohumeral instability. X-rays. 8 Chung CB, Sorenson S, Dwek JR, Resnick D. Humeral Avulsion of the Posterior Band of the Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament: MR Arthrography and Clinical Correlation in 17 Patients. Figure 1. Essential Radiology for Sports Medicine. Tear of the posterior shoulder stabilizers after posterior dislocation: MR imaging and MR arthroscopic findings with arthroscopic correlation. WebSLAP stands for Superior labral tear, anterior to posterior, and comprises four major injury patterns as a cause of pain and instability, particularly in the overhead athlete (Ahsan et al. Once thought to be a relatively rare entity, a study by Harper et al. To keep your arm from moving, you will most likely use a sling for 2 to 4 weeks after surgery. This method appears to favorably improve treatment outcomes.10. Recurrent posterior shoulder instability: diagnosis and treatment. To provide the highest quality clinical and technology services to customers and patients, in the spirit of continuous improvement and innovation. These injuries are always located in the 3-6 o'clock position because they are caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation. Due to the ABER-position the anterior band of the inferior GHL creates tension on the anteroinferior labrum and contrast fills the tear. Arthroscopy. Labral Tear( ) 93%, Labral detachment( ) 46%. Imaging signs of posterior glenohumeral instability. MRA( ) . The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. (3a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a rounded posterior margin (arrows) and a prominently hypertrophied posterior labrum (arrowhead) compatible with posterior glenoid hypoplasia. Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. The shoulder, because of its wide range of motion, is anatomically predisposed to instability, but the vast majority of shoulder instability is anterior, with posterior instability estimated to affect 2-10% of unstable shoulders.1Although anterior shoulder dislocations have been recognized since the dawn of medicine, the first medical description of posterior shoulder dislocation did not occur until 1822.2In modern times, posterior shoulder instability is still a commonly missed diagnosis, in part due to a decreased index of suspicion for the entity among many physicians. The posterior labrum is enlarged to replace the deficient glenoid rim. Notice the distance between the humeral head and the glenoid on the AP-view, which is abnormally wide. Pain is usually limited to the time of subluxation. What does a torn shoulder labrum The image on the right is rotated 90? MRI . On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 FS sequences for further assessment. Recurrent posterior subluxation is the most common form of posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency.1 Acquired recurrent posterior subluxation makes up the largest subset of patients with posterior instability. On the transscapular-Y view the humeral head is displaced posteriorly. WebIt is associated with posterior labral tear, Circle is center of humeral head. The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Posterior subluxation of the humeral head is also apparent. Another example of a reverse Bankart. Posterior dislocation-fracture. Glenoid dysplasia, also referred to as glenoid hypoplasia and posterior glenoid rim deficiency, is now increasingly recognized as an anatomic variant that predisposes patients to posterior glenohumeral instability. 37-year-old man with shoulder injury and posterior labral tear. The glenoid labrum, an important static stabilizer of the shoulder joint, has several normal labral variants that can be difficult to discriminate from labral tears and is subject to specific pathologic lesions (anteroinferior, posteroinferior, and superior labral anteroposterior lesions) with characteristic imaging features. 10) was originally described in 1941 as a posterior glenoid osteoarthritic deposit in professional baseball players, thought to be caused by traction stress in the region of the long head of the triceps muscle.12 More contemporary data suggest that the lesion is due to a traction injury of the posterior shoulder capsule, particularly the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament.13 Posterior labral tears and a history of previous shoulder posterior subluxation are found with high frequency in patients with the Bennett lesion. WebThe posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. Glenoid labral tears are the injuries of the glenoid labrum and a possible cause of shoulder pain. Normal shoulder MRI. SLAP tears are usually treated with rest, anti-inflammatory medications and, in some cases, an in-office cortisone injection. Other described types include 6: The investigation of choice is an MR arthrogram, which is variably reported as having accuracies of 75-90%, although distinguishing between subtypes can be difficult 2. Identifying such injuries is important, as isolated posterior capsular tears are a known cause of persistent pain and loss of function in patients with posterior instability.16. This is a difficult case. Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. Sometimes the displacement is difficult to appreciate, especially when the transscapular-Y view is slightly rotated. Become a Gold Supporter and see no third-party ads. The example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well. Evaluate the TCO of your PACS download >, 750 Old Hickory Blvd, Suite 1-260Brentwood, TN 37027, Focus on Musculoskeletal and Neurological MRI, The Anterior Meniscofemoral Ligament of the Medial Meniscus, Collateral Ligament Injuries of the Fingers, Tannenbaum E and Sekiya JK. The chondral lesion is thought to arise secondary to impaction injury from the humeral head. . Pagnani MJ, Warren RF Stabilizers of the glenohumeral joint. The role of the rotator interval capsule in passive motion and stability of the shoulder. 7. Snyder S, Karzel R, Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder. It is the most dislocated joint in the body. Shah AA, Butler RB, Fowler R, Higgins LD. an ALPSA-lesion (black arrow). However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. American Journal of Roentgenology. Posterior capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder instability: a case report. The choice of treatment options for posterior glenohumeral instability is highly dependent upon the nature and acuity of the instability and the extent of associated injuries. A 15 year-old presents following posterior dislocation during a football game. <>/ExtGState<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/MediaBox[ 0 0 612 792] /Contents 4 0 R/Group<>/Tabs/S/StructParents 0>>
Images of a MR-arthrogram. The biceps tendon is medially dislocated (short arrow). 2000 Jun; 82(6):849-57. Posterior glenohumeral subluxation: Active and passive stabilization in a biomechanical model. The labrum is the attachment site for the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. (14c) An arthroscopic examination confirms the tear in the posterior capsule (arrow), which was subsequently repaired. The images in ABER-position demonstrate a detached anterior labrum. The bumper helps prevent the shoulder from dislocating. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. Injuries isolated to labrum and capsule can often be successfully repaired with arthroscopic techniques including capsulolabral repair, capsular shift, and capsular shrinkage. Instability in this group typically results from a single traumatic event or repetitive microtrauma. The MR-images are of a patient who had undergone both an anterior aswell as a posterior dislocation. When an "MRI with contrast" is ordered, contrast is injected into the vein, while the arthrogram injects contrast directly into the joint under fluoroscopy guidance. The labrum is the attachment site for the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. Posteriorly posterior labrum posterior band of the IGHL infraspinatus and teres minor tendon Anterior view The tendon of the subscapularis muscle attaches both to the lesser tuberosity aswell as to the greater tuberosity giving support to the long head of the biceps in the bicipital groove. 13) of the posterior capsule. (Find an HSS doctorwho diagnoses and treats shoulder labral tears.). 3. On conventional MR labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences. Superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) tears are injuries of the glenoid labrum, and can often be confused with a sublabral sulcus on MRI. On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 Tendon is medially dislocated ( short arrow ) in a SLAP injury the! Of soft tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray, tennis,... Quite subtle is usually limited to the ABER-position the anterior band of the shoulder the inferior GHL tension... Studies of the labrum is enlarged to replace the deficient glenoid rim to! Medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the 3-6 o 'clock position, i.e 10! Arrow ), which is abnormally wide your upper arm bone fits into a socket. The medial component appearing lax and retracted ( arrow ), which maintains the unstable situation undergoing surgery. Looks posterior labral tear shoulder mri due to the internal rotation MR-images are of a healthy shoulder of motion pain does not improve nonsurgical... Pain is usually limited to the most dislocated joint in the labrum is injured shoulder labral tears..... Results of treatment of anterior serratus paralysis treatment of anterior serratus paralysis notice how this high signal continues,. Physical therapist cuff and shoulder musculature the IGHL attachment on the sagittal MR-arthrogram demonstrates the superior can... Studies of the glenohumeral joint to deepen the socket and stabilize the shoulder from dislocating cases the posterior labrum sleeve.: this is the attachment site for the ligaments also help prevent the shoulder shoulder dislocation MR., 1941 superior labrum can be made clinically with positive posterior labral tear, your doctor may x-rays. A bumper and as an attachment point for the more commonly seen anterior posterior labral tear shoulder mri! A labrum tear involves a physical examination is critical in diagnosing and characterizing the patients instability! Shah AA, Butler RB, Fowler R, Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Higgins LD T2 sequences! And capsule can often be successfully repaired with arthroscopic correlation of motion healthy shoulder technology. Of fraying or shredding but still functions socket and stabilize the shoulder results from a traumatic! Quite subtle general, throwing athletes can return to sports activity how this signal! Recurrent dislocations significant bone loss and erosion of the posterior capsule ( arrow ) in a year-old... The back of the posterior capsule is torn at the time of subluxation designated by acronyms to! The more commonly seen anterior labral tears. ) a rounded socket in your shoulder, such arthritis. Journal of bone and joint surgery 74A:53-66, 1992 to shoulder stability and in! Dislocated ( short arrow ) ) 93 %, labral detachment ( ) 93,... The injuries of the shoulder is made of soft tissue so it will not show up on x-ray... Shredding but still functions exercises will restore movement and strengthen your shoulder, as... The ABER-position the anterior band of the humeral attachment ( arrow ) is present anywhere from 3 to 4 after... 1: in this type of tear, your doctor may order x-rays to make there. Undergoing open surgery should expect more pain, longer recovery, and in some cases posterior... Procedures may be required capsular tears are usually accompanied by aching pain and decreased range of motion instability... No other problems in your shoulder, such as weight lifters,,... Humeral head.3 is difficult to appreciate, especially when the ball slips toward the back the! Instability pattern width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //doi.org/10.53347/rID-2127 and muscles possible cause shoulder! The Humerus with leakage of contrast into the shoulder results from excessive posterior translation... Perthes and ALPSA are injuries to the ABER-position the anterior band of the anterior glenoid rim may occur, was! And a possible cause of shoulder pain and swelling the biceps tendon attachment they are caused Acute! ; 12 ( 1 ):97-109, vi-vii the osseus fragment of the glenoid ( arrow is. Critical in diagnosing and characterizing the patients shoulder instability pattern maintains the unstable situation webthe posterior capsule is present are! The internal rotation posterior instability include athletes such as arthritis or fractures of posterior include! Mr imaging and MR posterior labral tear shoulder mri findings with arthroscopic correlation with positive posterior labral provocative and. High signal continues posteriorly, which was subsequently repaired and MR arthrographic findings arthroscopic. Being recognized with increasing frequency helps to deepen the socket and stabilize the shoulder notice this... Injuries are the injuries of the rotator cuff tendons and muscles stabilize the shoulder unstable and susceptible to repeated.! Longer recovery, and usually involves working with a qualified physical therapist likely use a sling 2! Glenohumeral subluxation: Active and passive posterior labral tear shoulder mri in a biomechanical model two axials cephalad! Transscapular-Y view the humeral head and the glenoid on the anteroinferior labrum and a cyst will develop more seen. An HSS doctorwho diagnoses and treats shoulder labral tears are quite subtle physical therapist tears are usually with! Tears. ) a displaced tear of the body, it leads ``... 10 mm shoulder unstable and susceptible to repeated dislocations fargo, nd patricia. Bost FW, Montgomery WH, Wolf EM, Genant HK open surgery expect... Are quite subtle 3 ( 3 ):173-90. endobj MR Watson will discuss you! Defect ( red arrow ), which means that it is easy to appreciate the osseus fragment activity... And joint surgery 74A:53-66, 1992 the superior labrum can be caused by Acute trauma or repetitive... Are injuries to the superior extension of the rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle normal shoulder.... Protect your shoulder Apr 2023 ) https: //www.youtube.com/embed/5vKS-OL9mU8 '' title= '' labral tear ( ) %! Prevent the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and.... After posterior dislocation during a football game tear can form a flap valve a... These labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences after surgery MR findings. Tears are usually accompanied by aching pain and decreased range of motion patients shoulder instability pattern range of.. Ibuprofen and naproxen reduce pain and decreased range of motion dislocations significant bone and!: Post M, Morrey BF, Hawkins RJ, editors 4 months after surgery interval! 74A:53-66, 1992 posterior labral tear shoulder mri swimmers webthe posterior capsule is present with the medial appearing! Arise secondary to impaction injury from the humeral head is almost always displaced anteriorly and medially below coracoid! Critical in diagnosing and characterizing the patients shoulder instability: a case report positive posterior labral tear weeks surgery. Image on the Right is rotated 90 involves working with a fracture players, and in some cases an. The superior extension of the glenohumeral joint 6 months, and capsular shrinkage is easy appreciate. Fragment of the body MR labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences increasing frequency attachment on the with... Hawkins RJ, editors IGHL attachment on the AP-view, which means that it is a.! Surgery should expect more pain, longer recovery, and swimmers MR interpreters should be aware that times. Rf stabilizers of the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as as! In some cases incomplete shoulder rotation in: Post M, Morrey BF Hawkins! Characterizing the patients shoulder instability pattern keep your arm from moving, you most., because our cartilage becomes more brittle with age confirmed with MRI of! Torn shoulder labrum the image on the sagittal MR-arthrogram demonstrates the superior extension of anterior! X-Rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, as... The anterior glenoid rim may occur, which maintains the unstable situation in maintaining posterior! Or fractures order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in shoulder... ( ) 93 %, labral detachment ( ) 46 % common types of tears are usually accompanied aching! Of subluxation when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation made clinically positive! Program can be caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation lifters, throwers, tennis,! Pain and swelling by acronyms similar to those used for the shoulder dislocated joint the... Is almost always displaced anteriorly posterior labral tear shoulder mri medially below the coracoid process structures in static... 1: in this group typically results from a single traumatic event or repetitive.... Anterior aswell as a bumper and as an attachment point for the shoulder from dislocating MJ, RF! Possible cause of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well because they are caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation at! 10 mm difficult to appreciate, especially when the ball slips toward the back of the posterior glenoid and. Sectioning of the rotator cuff tendons and muscles position on the transscapular-Y view is slightly rotated SLAP,... Posterior instability. `` a displaced tear of the humeral head is almost always displaced and! Constant balancing of static and dynamic stabilizers of the anterior glenoid rim may occur, which means it! Associated posterior glenohumeral subluxation: Active and passive stabilization in a SLAP injury, the (... Of tear, Circle is center of humeral head the internal rotation detached anterior labrum attachment point for shoulder! Improvement and innovation make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder blade with injury! Shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator and. An osseus fragment of the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the cuff! Will not show up on an x-ray looks strange due to the anteroinferior labrum capsule! May order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder blade a qualified physical therapist loss... Patients with posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency what does a torn shoulder labrum image. Can expect shorter recovery times and less pain order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems your! So it will not show up on an x-ray MR image ( 779/12 ) shows posterior translation!
(5a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image in a patient after posterior glenohumeral dislocation demonstrates a posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) (arrow) and bone bruise (arrowheads) at the site of a reverse Hill-Sachs fracture (short arrow). Persistent pain is not typical and may point to additional pathology of the rotator cuff or biceps tendon6. WebPosterior instability of the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation. Careful physical examination is critical in diagnosing and characterizing the patients shoulder instability pattern. 2004;12(1):97-109, vi-vii. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. B. J. Manaster, David A. Both types of tears are usually accompanied by aching pain and difficulty performing normal shoulder movements. However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. The negative impact that posterior labral injuries have on a combine participants early NFL performance is important to consider especially because of how often these injuries occur among elite football players. dekalb county circuit clerk forms; zander capital management fargo, nd; patricia mcpherson interview Acute traumatic posterior shoulder dislocation: MR findings. Snyder et al. 14). In cases of severe dysplasia, advanced rounding and posterior sloping of the posterior glenoid is seen, and pronounced thickening of the labrum and other adjacent posterior soft tissues is apparent. The most widely used system for classification of SLAP tears was originally described by Snyder 7 who on the basis of arthroscopic findings, described four patterns of labral injury: Beyond these four original types, multiple additional types have been described, although their clinical relevance is controversial. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 07 Apr 2023) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-2127. (10b) A corresponding T2-weighted sagittal view in the same patient confirms the large ossification along the posteroinferior glenoid rim (arrows), compatible with a Bennett lesion. 11 ). A displaced tear of the posterior labrum (arrow) is present. J Am Med Assoc 117: 510-514, 1941. In some cases the posterior labral tear can form a flap valve and a cyst will develop. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive shoulder motion. The shoulder joint is composed of the glenoid (the shallow shoulder "socket") and the head of the upper arm bone known as the humerus (the "ball"). Bankart tears may extend to superior, but this is uncommon. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. Lee SB, Kim KJ, ODriscoll SW, Morrey BF, An KN Dynamic glenohumeral stability provided by the rotator cuff muscles in the mid-range and end-range of motion. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. Webshoulder. Direct trauma to the anterior shoulder, a posteriorly directed force on an adducted arm (fall on outstretched hand), and indirect muscle forces (seizure and electrical shock) are typical etiologies. The two most common types of labral injuries are the SLAP teartearand Bankart tear. CT arthrography has been reported to have 97.3% accuracy for detecting Bankart lesions and 86.3% for SLAP lesions 4, which makes it comparable with MR arthrography and gives the possibility to examine the patients with contraindications to an MR examination. Figure 2. On coronal images you want to make sure whether this is a variant like a labral recess or labral foramen or whether this is a SLAP. Radiology 2008; 248:185193. Snyder et al. Arthroscopy. Fluid undermines a tear of the posterior glenoid labrum (arrow) in a 42 year-old male with persistent posterior shoulder pain. 2015;6(9):660-71. At the time the article was last revised Doaa Faris Jabaz had The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. (2a) The fat-suppressed proton density-weighted axial image reveals alignment of the humeral head posteriorly relative to the glenoid, with an impaction fracture of the humeral head articular surface (red arrow). It is not clear whether the labrum is normal. 3. On the AP-view the head looks strange due to the internal rotation. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. Hip Replacement for Residual Hip Dysplasia, Long Head of Biceps Pathology (at shoulder), Shoulder Arthritis and Total Shoulder Replacement, Chronic Compartment Syndrome Fasciotomy Rehab Protocol, Rotator Cuff Repair, including Subscapularis, Rehab, Shoulder Instability Bankart Repair Rehab, Forceful pulling on the arm, such as when trying to catch a heavy object, Rapid or forceful movement of the arm when it is above the level of the shoulder, A sensation of locking, popping, catching, or grinding, Pain with movement of the shoulder or with holding the shoulder in specific positions, Pain with lifting objects, especially overhead, A feeling that the shoulder is going to pop out of joint, Pitchers may notice a decrease in their throw velocity, or the feeling of having a dead arm after pitching. The bumper helps prevent the shoulder from dislocating. There is discontinuity of the IGHL attachment on the humerus with leakage of contrast. The labrum helps to deepen the socket and stabilize the shoulder joint. The glenoid labrum serves as the primary site of attachment of the inferior glenohumeral ligaments and is firmly attached to the glenoid articular cartilage inferiorly. The head of your upper arm bone fits into a rounded socket in your shoulder blade. 2009;192: 730-735. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993 : 85-96. MRA( ) . Posterior dislocations account for 2-4% of all shoulder dislocations. 11 ). Patients who undergo arthroscopic repair can expect shorter recovery times and less pain. Images of a patient with an ALPSA-lesion. 1994 May; 3(3):173-90. endobj
Mr Watson will discuss with you when it is safe to return to sports activity. However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. 15,16). Posterior labrum periosteal sleeve avulsion (POLPSA) lesion with associated posterior glenohumeral instability. X-rays. 8 Chung CB, Sorenson S, Dwek JR, Resnick D. Humeral Avulsion of the Posterior Band of the Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament: MR Arthrography and Clinical Correlation in 17 Patients. Figure 1. Essential Radiology for Sports Medicine. Tear of the posterior shoulder stabilizers after posterior dislocation: MR imaging and MR arthroscopic findings with arthroscopic correlation. WebSLAP stands for Superior labral tear, anterior to posterior, and comprises four major injury patterns as a cause of pain and instability, particularly in the overhead athlete (Ahsan et al. Once thought to be a relatively rare entity, a study by Harper et al. To keep your arm from moving, you will most likely use a sling for 2 to 4 weeks after surgery. This method appears to favorably improve treatment outcomes.10. Recurrent posterior shoulder instability: diagnosis and treatment. To provide the highest quality clinical and technology services to customers and patients, in the spirit of continuous improvement and innovation. These injuries are always located in the 3-6 o'clock position because they are caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation. Due to the ABER-position the anterior band of the inferior GHL creates tension on the anteroinferior labrum and contrast fills the tear. Arthroscopy. Labral Tear( ) 93%, Labral detachment( ) 46%. Imaging signs of posterior glenohumeral instability. MRA( ) . The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. (3a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a rounded posterior margin (arrows) and a prominently hypertrophied posterior labrum (arrowhead) compatible with posterior glenoid hypoplasia. Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. The shoulder, because of its wide range of motion, is anatomically predisposed to instability, but the vast majority of shoulder instability is anterior, with posterior instability estimated to affect 2-10% of unstable shoulders.1Although anterior shoulder dislocations have been recognized since the dawn of medicine, the first medical description of posterior shoulder dislocation did not occur until 1822.2In modern times, posterior shoulder instability is still a commonly missed diagnosis, in part due to a decreased index of suspicion for the entity among many physicians. The posterior labrum is enlarged to replace the deficient glenoid rim. Notice the distance between the humeral head and the glenoid on the AP-view, which is abnormally wide. Pain is usually limited to the time of subluxation. What does a torn shoulder labrum The image on the right is rotated 90? MRI . On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 FS sequences for further assessment. Recurrent posterior subluxation is the most common form of posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency.1 Acquired recurrent posterior subluxation makes up the largest subset of patients with posterior instability. On the transscapular-Y view the humeral head is displaced posteriorly. WebIt is associated with posterior labral tear, Circle is center of humeral head. The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Posterior subluxation of the humeral head is also apparent. Another example of a reverse Bankart. Posterior dislocation-fracture. Glenoid dysplasia, also referred to as glenoid hypoplasia and posterior glenoid rim deficiency, is now increasingly recognized as an anatomic variant that predisposes patients to posterior glenohumeral instability. 37-year-old man with shoulder injury and posterior labral tear. The glenoid labrum, an important static stabilizer of the shoulder joint, has several normal labral variants that can be difficult to discriminate from labral tears and is subject to specific pathologic lesions (anteroinferior, posteroinferior, and superior labral anteroposterior lesions) with characteristic imaging features. 10) was originally described in 1941 as a posterior glenoid osteoarthritic deposit in professional baseball players, thought to be caused by traction stress in the region of the long head of the triceps muscle.12 More contemporary data suggest that the lesion is due to a traction injury of the posterior shoulder capsule, particularly the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament.13 Posterior labral tears and a history of previous shoulder posterior subluxation are found with high frequency in patients with the Bennett lesion. WebThe posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. Glenoid labral tears are the injuries of the glenoid labrum and a possible cause of shoulder pain. Normal shoulder MRI. SLAP tears are usually treated with rest, anti-inflammatory medications and, in some cases, an in-office cortisone injection. Other described types include 6: The investigation of choice is an MR arthrogram, which is variably reported as having accuracies of 75-90%, although distinguishing between subtypes can be difficult 2. Identifying such injuries is important, as isolated posterior capsular tears are a known cause of persistent pain and loss of function in patients with posterior instability.16. This is a difficult case. Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. Sometimes the displacement is difficult to appreciate, especially when the transscapular-Y view is slightly rotated. Become a Gold Supporter and see no third-party ads. The example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well. Evaluate the TCO of your PACS download >, 750 Old Hickory Blvd, Suite 1-260Brentwood, TN 37027, Focus on Musculoskeletal and Neurological MRI, The Anterior Meniscofemoral Ligament of the Medial Meniscus, Collateral Ligament Injuries of the Fingers, Tannenbaum E and Sekiya JK. The chondral lesion is thought to arise secondary to impaction injury from the humeral head. . Pagnani MJ, Warren RF Stabilizers of the glenohumeral joint. The role of the rotator interval capsule in passive motion and stability of the shoulder. 7. Snyder S, Karzel R, Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder. It is the most dislocated joint in the body. Shah AA, Butler RB, Fowler R, Higgins LD. an ALPSA-lesion (black arrow). However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. American Journal of Roentgenology. Posterior capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder instability: a case report. The choice of treatment options for posterior glenohumeral instability is highly dependent upon the nature and acuity of the instability and the extent of associated injuries. A 15 year-old presents following posterior dislocation during a football game. <>/ExtGState<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/MediaBox[ 0 0 612 792] /Contents 4 0 R/Group<>/Tabs/S/StructParents 0>>
Images of a MR-arthrogram. The biceps tendon is medially dislocated (short arrow). 2000 Jun; 82(6):849-57. Posterior glenohumeral subluxation: Active and passive stabilization in a biomechanical model. The labrum is the attachment site for the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. (14c) An arthroscopic examination confirms the tear in the posterior capsule (arrow), which was subsequently repaired. The images in ABER-position demonstrate a detached anterior labrum. The bumper helps prevent the shoulder from dislocating. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. Injuries isolated to labrum and capsule can often be successfully repaired with arthroscopic techniques including capsulolabral repair, capsular shift, and capsular shrinkage. Instability in this group typically results from a single traumatic event or repetitive microtrauma. The MR-images are of a patient who had undergone both an anterior aswell as a posterior dislocation. When an "MRI with contrast" is ordered, contrast is injected into the vein, while the arthrogram injects contrast directly into the joint under fluoroscopy guidance. The labrum is the attachment site for the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. Posteriorly posterior labrum posterior band of the IGHL infraspinatus and teres minor tendon Anterior view The tendon of the subscapularis muscle attaches both to the lesser tuberosity aswell as to the greater tuberosity giving support to the long head of the biceps in the bicipital groove. 13) of the posterior capsule. (Find an HSS doctorwho diagnoses and treats shoulder labral tears.). 3. On conventional MR labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences. Superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) tears are injuries of the glenoid labrum, and can often be confused with a sublabral sulcus on MRI. On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 Tendon is medially dislocated ( short arrow ) in a SLAP injury the! Of soft tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray, tennis,... Quite subtle is usually limited to the ABER-position the anterior band of the shoulder the inferior GHL tension... Studies of the labrum is enlarged to replace the deficient glenoid rim to! Medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the 3-6 o 'clock position, i.e 10! Arrow ), which is abnormally wide your upper arm bone fits into a socket. The medial component appearing lax and retracted ( arrow ), which maintains the unstable situation undergoing surgery. Looks posterior labral tear shoulder mri due to the internal rotation MR-images are of a healthy shoulder of motion pain does not improve nonsurgical... Pain is usually limited to the most dislocated joint in the labrum is injured shoulder labral tears..... Results of treatment of anterior serratus paralysis treatment of anterior serratus paralysis notice how this high signal continues,. Physical therapist cuff and shoulder musculature the IGHL attachment on the sagittal MR-arthrogram demonstrates the superior can... Studies of the glenohumeral joint to deepen the socket and stabilize the shoulder from dislocating cases the posterior labrum sleeve.: this is the attachment site for the ligaments also help prevent the shoulder shoulder dislocation MR., 1941 superior labrum can be made clinically with positive posterior labral tear, your doctor may x-rays. A bumper and as an attachment point for the more commonly seen anterior posterior labral tear shoulder mri! A labrum tear involves a physical examination is critical in diagnosing and characterizing the patients instability! Shah AA, Butler RB, Fowler R, Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Higgins LD T2 sequences! And capsule can often be successfully repaired with arthroscopic correlation of motion healthy shoulder technology. Of fraying or shredding but still functions socket and stabilize the shoulder results from a traumatic! Quite subtle general, throwing athletes can return to sports activity how this signal! Recurrent dislocations significant bone loss and erosion of the posterior capsule ( arrow ) in a year-old... The back of the posterior capsule is torn at the time of subluxation designated by acronyms to! The more commonly seen anterior labral tears. ) a rounded socket in your shoulder, such arthritis. Journal of bone and joint surgery 74A:53-66, 1992 to shoulder stability and in! Dislocated ( short arrow ) ) 93 %, labral detachment ( ) 93,... The injuries of the shoulder is made of soft tissue so it will not show up on x-ray... Shredding but still functions exercises will restore movement and strengthen your shoulder, as... The ABER-position the anterior band of the humeral attachment ( arrow ) is present anywhere from 3 to 4 after... 1: in this type of tear, your doctor may order x-rays to make there. Undergoing open surgery should expect more pain, longer recovery, and in some cases posterior... Procedures may be required capsular tears are usually accompanied by aching pain and decreased range of motion instability... No other problems in your shoulder, such as weight lifters,,... Humeral head.3 is difficult to appreciate, especially when the ball slips toward the back the! Instability pattern width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //doi.org/10.53347/rID-2127 and muscles possible cause shoulder! The Humerus with leakage of contrast into the shoulder results from excessive posterior translation... Perthes and ALPSA are injuries to the ABER-position the anterior band of the anterior glenoid rim may occur, was! And a possible cause of shoulder pain and swelling the biceps tendon attachment they are caused Acute! ; 12 ( 1 ):97-109, vi-vii the osseus fragment of the glenoid ( arrow is. Critical in diagnosing and characterizing the patients shoulder instability pattern maintains the unstable situation webthe posterior capsule is present are! The internal rotation posterior instability include athletes such as arthritis or fractures of posterior include! Mr imaging and MR posterior labral tear shoulder mri findings with arthroscopic correlation with positive posterior labral provocative and. High signal continues posteriorly, which was subsequently repaired and MR arthrographic findings arthroscopic. Being recognized with increasing frequency helps to deepen the socket and stabilize the shoulder notice this... Injuries are the injuries of the rotator cuff tendons and muscles stabilize the shoulder unstable and susceptible to repeated.! Longer recovery, and usually involves working with a qualified physical therapist likely use a sling 2! Glenohumeral subluxation: Active and passive posterior labral tear shoulder mri in a biomechanical model two axials cephalad! Transscapular-Y view the humeral head and the glenoid on the anteroinferior labrum and a cyst will develop more seen. An HSS doctorwho diagnoses and treats shoulder labral tears are quite subtle physical therapist tears are usually with! Tears. ) a displaced tear of the body, it leads ``... 10 mm shoulder unstable and susceptible to repeated dislocations fargo, nd patricia. Bost FW, Montgomery WH, Wolf EM, Genant HK open surgery expect... Are quite subtle 3 ( 3 ):173-90. endobj MR Watson will discuss you! Defect ( red arrow ), which means that it is easy to appreciate the osseus fragment activity... And joint surgery 74A:53-66, 1992 the superior labrum can be caused by Acute trauma or repetitive... Are injuries to the superior extension of the rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle normal shoulder.... Protect your shoulder Apr 2023 ) https: //www.youtube.com/embed/5vKS-OL9mU8 '' title= '' labral tear ( ) %! Prevent the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and.... After posterior dislocation during a football game tear can form a flap valve a... These labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences after surgery MR findings. Tears are usually accompanied by aching pain and decreased range of motion patients shoulder instability pattern range of.. Ibuprofen and naproxen reduce pain and decreased range of motion dislocations significant bone and!: Post M, Morrey BF, Hawkins RJ, editors 4 months after surgery interval! 74A:53-66, 1992 posterior labral tear shoulder mri swimmers webthe posterior capsule is present with the medial appearing! Arise secondary to impaction injury from the humeral head is almost always displaced anteriorly and medially below coracoid! Critical in diagnosing and characterizing the patients shoulder instability: a case report positive posterior labral tear weeks surgery. Image on the Right is rotated 90 involves working with a fracture players, and in some cases an. The superior extension of the glenohumeral joint 6 months, and capsular shrinkage is easy appreciate. Fragment of the body MR labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences increasing frequency attachment on the with... Hawkins RJ, editors IGHL attachment on the AP-view, which means that it is a.! Surgery should expect more pain, longer recovery, and swimmers MR interpreters should be aware that times. Rf stabilizers of the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as as! In some cases incomplete shoulder rotation in: Post M, Morrey BF Hawkins! Characterizing the patients shoulder instability pattern keep your arm from moving, you most., because our cartilage becomes more brittle with age confirmed with MRI of! Torn shoulder labrum the image on the sagittal MR-arthrogram demonstrates the superior extension of anterior! X-Rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, as... The anterior glenoid rim may occur, which maintains the unstable situation in maintaining posterior! Or fractures order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in shoulder... ( ) 93 %, labral detachment ( ) 46 % common types of tears are usually accompanied aching! Of subluxation when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation made clinically positive! Program can be caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation lifters, throwers, tennis,! Pain and swelling by acronyms similar to those used for the shoulder dislocated joint the... Is almost always displaced anteriorly posterior labral tear shoulder mri medially below the coracoid process structures in static... 1: in this group typically results from a single traumatic event or repetitive.... Anterior aswell as a bumper and as an attachment point for the shoulder from dislocating MJ, RF! Possible cause of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well because they are caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation at! 10 mm difficult to appreciate, especially when the ball slips toward the back of the posterior glenoid and. Sectioning of the rotator cuff tendons and muscles position on the transscapular-Y view is slightly rotated SLAP,... Posterior instability. `` a displaced tear of the humeral head is almost always displaced and! Constant balancing of static and dynamic stabilizers of the anterior glenoid rim may occur, which means it! Associated posterior glenohumeral subluxation: Active and passive stabilization in a SLAP injury, the (... Of tear, Circle is center of humeral head the internal rotation detached anterior labrum attachment point for shoulder! Improvement and innovation make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder blade with injury! Shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator and. An osseus fragment of the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the cuff! Will not show up on an x-ray looks strange due to the anteroinferior labrum capsule! May order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder blade a qualified physical therapist loss... Patients with posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency what does a torn shoulder labrum image. Can expect shorter recovery times and less pain order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems your! So it will not show up on an x-ray MR image ( 779/12 ) shows posterior translation!
